

read more along with inadequate expiratory time and autoPEEP too low a rate risks inadequate minute ventilation and respiratory acidosis Respiratory Acidosis Respiratory acidosis is primary increase in carbon dioxide partial pressure (Pco2) with or without compensatory increase in bicarbonate (HCO3 −) pH is usually low but may be near. Too high a rate risks hyperventilation and respiratory alkalosis Respiratory Alkalosis Respiratory alkalosis is a primary decrease in carbon dioxide partial pressure (Pco2) with or without compensatory decrease in bicarbonate (HCO3 −) pH may be high or near normal.
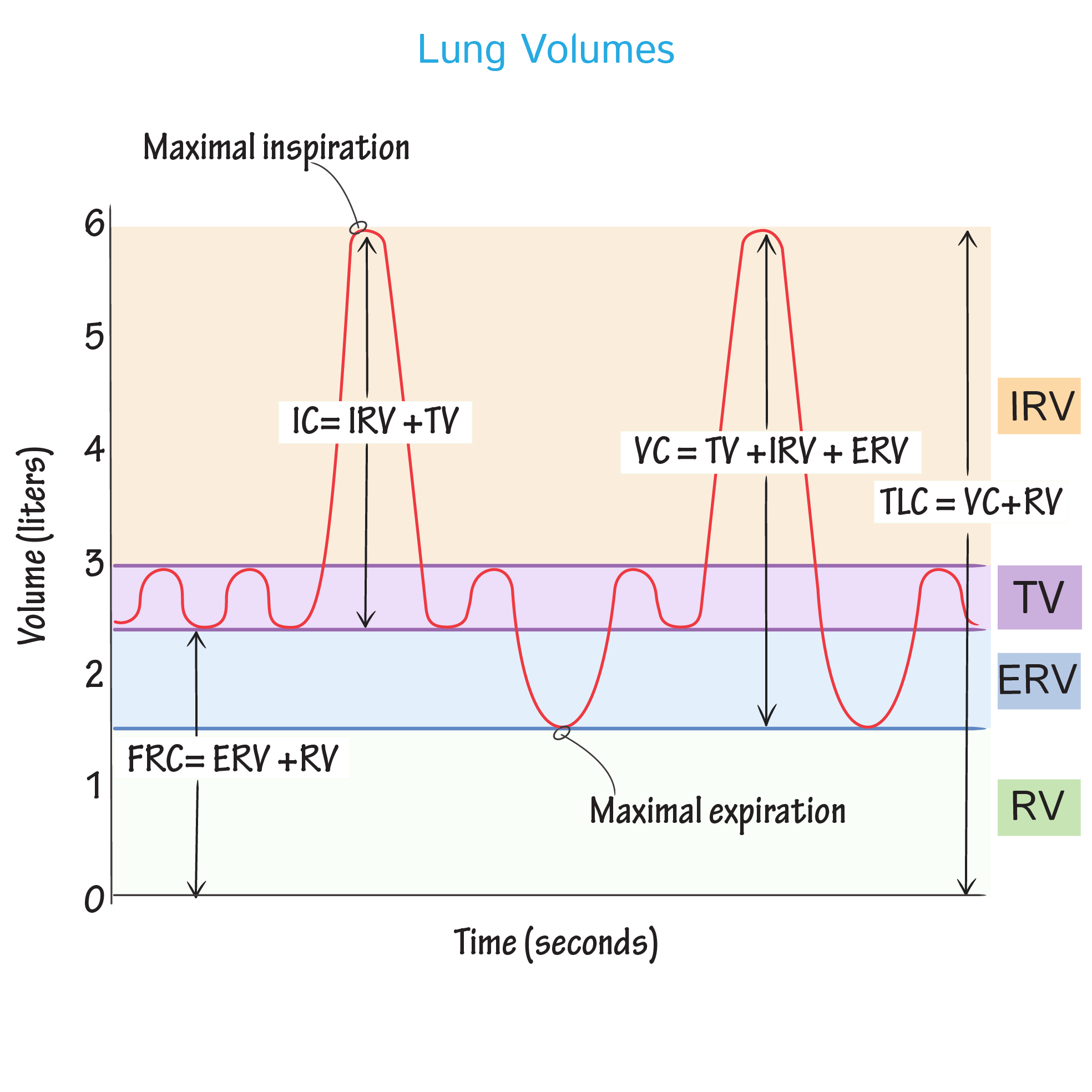
Patients may have dyspnea or respiratory failure if atelectasis is extensive. Too high a volume risks overinflation too low a volume allows for atelectasis Atelectasis Atelectasis is collapse of lung tissue with loss of volume. Tidal volume and respiratory rate set the minute ventilation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
